As you know one of the main challenges facing humankind is now air pollution, with transport estimated to contribute to a considerable percentage of carbon dioxide produced annually. Dependence on gasoline to power cars has had severe negative impacts on the environment, as it produces CO2 and other greenhouse gases. Carbon dioxide emissions affect the climate, thus affecting food production. Also, greenhouse gases’ emissions are highly associated with global warming.
Electric and hybrid cars play a crucial role in solving key ecological problems. Environmentally-friendly cars have become increasingly popular in recent years as more consumers face growing concerns about the environmental effects of conventional vehicles. Driving a hybrid car instead of a traditional one helps remove large amounts of carbon from the atmosphere.
ICE gives way to EV, Hybrid!
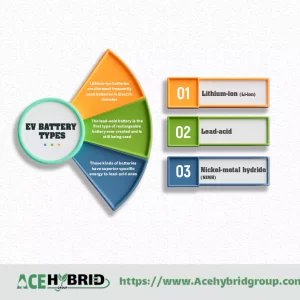
To replace internal combustion engines, ICEs, in regular cars, electric vehicles, EVs, were developed. Electric cars are battery-powered, charged by connecting to a power source. But the problem is that demand for electric cars is low. The lack of infrastructure of charging stations in many countries of the world, high cost, and inability to travel long distances lessen the popularity of electric cars. So we needed to tackle these shortcomings. To that end, hybrid vehicles were developed. Hybrids consist of a conventional internal combustion engine and an electric propulsion motor.
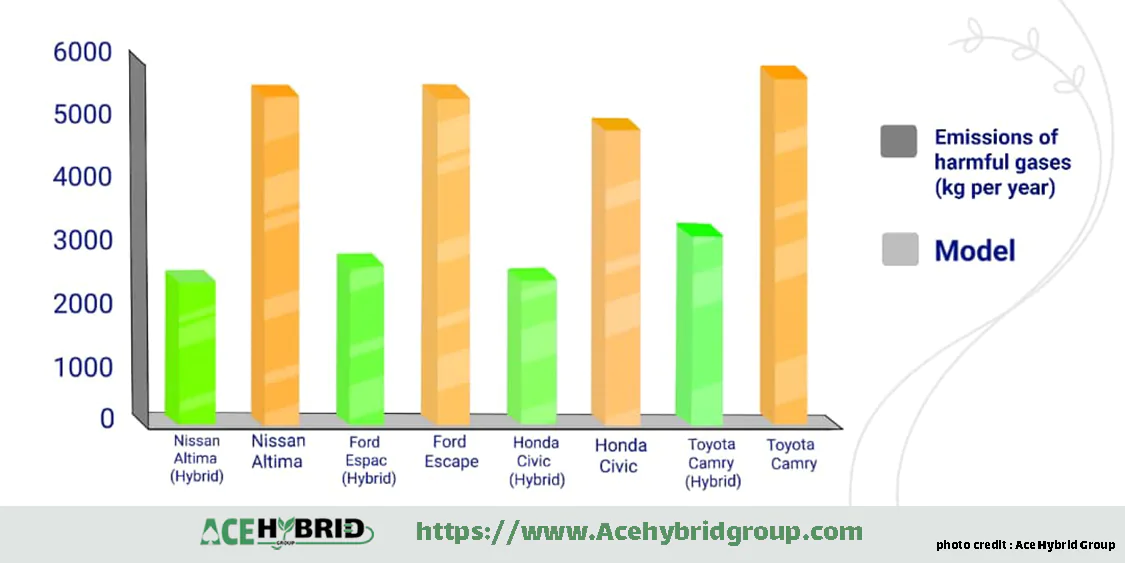
So plug-in hybrids utilize both gasoline and a rechargeable electric motor to power it, and as a result, they contribute to lower amounts of emissions. A hybrid car can emit approximately 46 % less greenhouse gas than a traditional vehicle. Hybrid vehicles produce less emission gases, because they burn and use less fuel, and this helps protect ozone. As long as people keep buying hybrids, there would be signs of air pollution reduction. The other element that makes hybrids beneficial to the environment is electricity, since electricity does not harm it. Using electricity alone in hybrid cars is a feature, suitable for city driving, i.e., driving at short distances and at low speeds. The bottomline is that hybrid vehicles are highly sought-after thanks to the combination of efficiency and ecological benefits. They mark a very significant step towards a zero carbon, one hundred percent renewable future.
credit: Porokhnya, A. and Oganisyan, A., 2022, February. Hybrid cars–solution to ecological challenges. Optimizing maintenance regimes for hybrid vehicles.
 Ace Hybrid Tech | Hybrid battery replacement
Ace Hybrid Tech | Hybrid battery replacement