The increasing concerns about energy and environmental policies in the automotive industry have led to the development of renewable technology in hybrid vehicles. Undesirable emissions from internal combustion engines have raised health and environmental issues, driving the need for a shift towards zero-emission vehicles like electric vehicles (EVs). Hybrid car batteries play a crucial role in powering these eco-friendly vehicles. Understanding how temperature fluctuations impact car batteries is essential for maintaining battery health and prolonging their lifespan. Consequently, their thermal management is critical, as extreme temperatures affect their performance, efficiency, and overall driving range. Various studies have explored thermal management techniques to optimize EV battery systems, and we intend to cover these findings in our upcoming blog posts.
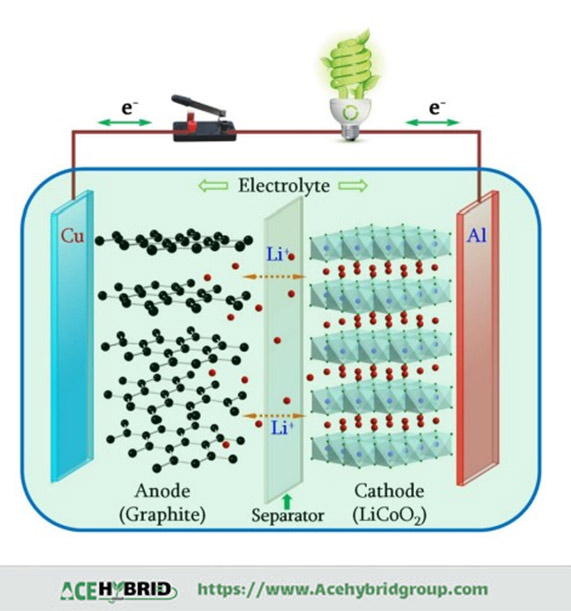
To begin, we will take a quick look at lithium-ion batteries to comprehend the temperature effects on cells and internal reactions. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used in electric vehicles. A lithium-ion rechargeable battery comprises three main components: a cathode, an anode, and an electrolyte containing lithium salt in a non-aqueous organic solvent which electrodes are immersed in and separated by a polymer membrane. The electrolyte must have high ionic conductivity, low viscosity, and minimal volume, achieved using a mixture of solvents. The interaction between the cathode, anode, and electrolyte enables the lithium-ion battery to store and release electrical energy efficiently. Additionally, a separator with a permeable membrane is placed between the cathode and anode to prevent direct contact and short circuits while allowing lithium ions to flow. The configuration of rechargeable Li-ion batteries is shown in the figure below.
This blog explores the effects of hot and cold weather on EV batteries and offers valuable insights into optimizing battery health for better driving experiences.
Temperatures Effect on Electric Vehicle Batteries
The internal and external temperatures of electric vehicle (EV) batteries are crucial factors that directly impact battery performance, efficiency, and safety. This is a primary concern for consumers regarding electric or hybrid vehicles. Let’s explore the significance of internal and external temperatures in the context of EV batteries:
Internal Temperature of EV Batteries:
- Optimal operating temperature: EV batteries perform optimally within a specific temperature range. Generally, most lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in EVs, operate best between 20°C to 35°C or 68°F to 95°F (By reviewing the literature, it appears that there is very little variation within the range being studied). Operating within this range ensures efficient charging and discharging, maximizing battery life and capacity.
- Temperature rise during charging/discharging: During the charging and discharging processes, EV batteries generate heat. Managing the internal temperature is critical to prevent overheating and thermal runaway, which can lead to safety hazards and reduce battery lifespan.
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Advanced EVs are equipped with sophisticated Battery Management Systems that monitor and control the internal temperature of the battery cells. BMS ensures even temperature distribution across cells, prevents over-charging/over-discharging, and initiates thermal management measures when required.
External Temperature of EV Batteries:
- Impact on range and efficiency: External temperatures can affect an electric vehicle’s efficiency. In extreme cold, battery performance may reduce, leading to decreased driving range. Similarly, in high temperatures, battery degradation may occur faster.
- Thermal management systems[1]: To regulate the external temperature, EVs are equipped with thermal management systems, including different types of methods. These systems help maintain the battery at optimal temperatures for improved performance and longevity.
- Fast charging and temperature: Fast charging, while convenient, can generate more heat in the battery. Careful thermal management is crucial during fast charging to prevent thermal stress and ensure battery safety.
Overall, maintaining both internal and external temperatures within the optimal range is essential for the efficient and safe operation of electric vehicle batteries. Advances in thermal management technologies and battery materials continue to improve battery performance, making electric vehicles increasingly reliable and practical for daily use. Some studies cover the latest developments and advancements in thermal management systems for EV batteries, focusing on techniques to regulate and maintain battery temperature within an optimal range. Various thermal management strategies, such as liquid cooling, air cooling, and phase-change materials, are explored to demonstrate their effectiveness in controlling battery temperature during charging, discharging, and other operating conditions (For more information, follow the references).
Advanced thermal management systems are critical to maintaining safe operating temperatures. Various thermal management techniques are employed in electric vehicles (EVs) to ensure optimal performance and safety of the battery systems since effective thermal management is essential to address temperature-related challenges.
Hot Weather Impact on EV Batteries:
Hot weather significantly impacts electric vehicle (EV) batteries, affecting their performance and overall health. Extremely high temperatures can be hazardous to EV batteries, and in rare cases, they may lead to thermal runaway or battery fires.
Here are some impacts of hot weather on EV batteries:
- Battery degradation: Exposure to high temperatures can accelerate chemical reactions inside the battery, leading to cracking and fragmentation of the electrode layer.
- Thermal runaway: Extreme heat can trigger thermal runaway, a critical condition where the battery overheats and rapidly releases energy. Thermal runaway can lead to battery failure and pose safety risks.
- Capacity fade: In hot weather, the battery’s capacity may decrease over time due to increased internal resistance and chemical reactions. This capacity fade means the battery can hold less charge, reducing driving range per charge.
- Faster aging: The battery’s aging process is accelerated in hot conditions. Higher temperatures cause the battery’s active materials to deteriorate more quickly, resulting in a shorter usable life.
- Charging challenges: Charging batteries in hot weather is less efficient and can cause overcharging, damaging the battery and reducing capacity.
- Cooling demands: In hot climates, EVs may require more energy to cool the battery, increasing power consumption and potentially reducing the driving range.
In hot weather, taking precautions for EVs is essential to protect the battery and maximize its performance. Here are some precautions to consider:
- Park in Shaded Areas
- Pre-condition the Battery: Many modern EVs have pre-conditioning features that allow you to cool down the battery before driving in hot weather.
- Avoid rapid charging in extreme heat
- Limit high-speed driving
- Check tire pressure
- Plan charging strategically: Charge your EV during cooler times of the day or at night to avoid high temperatures during the charging process.
- Monitor Battery Health: Keep an eye on your EV’s battery health. If you notice any unusual changes in battery performance or range, then have it checked by a technician.
Cold Weather Impact on Hybrid Car Batteries
Sub-zero temperatures are ordinary in North America, especially in Canada and many European countries. In such cold climates, the design of batteries becomes critical as temperature fluctuations can cause setbacks. Low temperatures harm the battery’s energy levels, increasing its internal impedance and degradation of the battery cells. As well, low temperatures can affect the charge-transfer kinetics. These factors can significantly impact the EV battery’s performance over its entire lifespan. In general terms, factors like cell design, shape, and the suitability of the electrolytic solution in cold environments are cited as contributing to this issue.
Here are some key impacts of low temperatures on EV batteries:
- Reduced battery life and degradation: Exposure to low temperatures slow down chemical reactions inside the battery, resulting in decreased electrical output. This accelerates battery degradation over time, reducing the battery’s overall lifespan.
- Reduced Range: In cold weather, the driving range of electric vehicles can decrease significantly. Lower temperatures cause the battery’s internal resistance to increase, which hinders the flow of electrons and reduces the battery’s capacity to store and deliver energy. As a result, EVs may have a shorter driving range per charge during cold weather conditions.
- Slower charging: Cold temperatures can slow down the charging process of EV batteries. The increased internal resistance leads to slower charging rates, making it take longer to recharge the battery to its total capacity.
- Regenerative braking limitations: Regenerative braking, which helps recover energy during deceleration and braking, may be limited in cold temperatures. The battery’s ability to accept energy during regenerative braking can be hampered, leading to less efficient energy recapture.
- Reduced power output: Cold temperatures can impact the power output of electric vehicle batteries. The battery’s ability to deliver high power, such as during rapid acceleration or climbing steep inclines, may be compromised in cold weather.
Taking precautions for EVs in cold weather is essential to ensure optimal battery performance and range. Here are some precautions to consider:
- Pre-Condition the Battery: Use the pre-conditioning feature available in many EVs to warm up the battery before driving. Pre-conditioning helps improve battery efficiency and range in cold weather.
- Park in Heated Areas
- Drive Moderately: Aggressive driving can decrease the driving range in cold weather. Drive at a moderate speed to conserve energy and maximize battery efficiency.
- Maintain proper tire pressure
- Plan charging strategically: Charge your EV in a heated garage or use a preconditioning feature before charging to ensure optimal battery temperature during the charging process.
- Monitor Battery Health: Keep an eye on your EV’s battery health. If you notice any unusual changes in battery performance or range, check it with a technician.
To mitigate the impact of high and low temperatures on EV batteries, manufacturers implement thermal management systems to regulate battery temperature and optimize performance.
Conclusion
Studies suggest that EV batteries operate most efficiently in optimum climatic regions, highlighting the importance of temperature considerations for battery performance in real-world applications. Extreme temperatures can significantly impact the performance and lifespan of car batteries.
Whether in extreme heat or freezing cold, proper battery maintenance and precautionary measures are crucial to ensure optimal battery health and functionality. Also, regular maintenance is vital to mitigate extreme temperatures’ impact on car batteries. By understanding and addressing the challenges posed by temperature fluctuations, we can make our car batteries more resilient and reliable, ultimately enhancing our driving experience and avoiding unexpected breakdowns.
Remember always to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for battery care and consult a professional if you have specific concerns about your car battery’s performance in extreme weather conditions.
“Feel free to contact us with any specific concerns or questions about this or any other issue. Our team is here to assist and provide you with the necessary information and support you need.”
 Ace Hybrid Tech | Hybrid battery replacement
Ace Hybrid Tech | Hybrid battery replacement