In recent years most countries have taken steps to find cleaner ways of fueling cars. In doing so, different types of fuels have been considered to replace the old ones in automobiles. They have one thing in common and that’s the ability to not be reliant on non-renewable fuels. Electricity is one of them. But gasoline can not be directly converted to electricity, because it is a manufactured product. It ‘s hydrocarbon fuel that must be converted into electricity through combustion. However hydrocarbon combustion produces three products of carbon dioxide, water and heat, resulting in efficiency losses.
BATTERY-ELECTRIC VEHICLE HELPFUL?
BEVs are powered entirely by electricity. They do not contain an internal combustion engine, take no gasoline, and have no exhaust pipe. Instead they have one or more electric motors which are powered by a large onboard battery. If we measure the efficiency of the vehicles, BEVs are about four times more efficient than regular cars. The high efficiency of BEVs is related to the fact that only very little energy is wasted in the drivetrain. In contrast, internal
combustion vehicles have major losses in efficiency. Although gasoline has high energy density, burning it is not efficient. Battery electrics are simpler and efficient. So banning the sale of new
petrol and diesel cars and replacing them with electric cars will be a great help. Nevertheless, electric vehicles face big challenges. These challenges include customer acceptance, high costs, poor charging infrastructure, need for battery replacement as well as finite minerals and rare metals.
For instance, just in the U.S. to convert the entire passenger car and commercial fleets from internal combustion to battery-electric will require the following:
- Billions of tons of copper, aluminium, steel and concrete to build a new high capacity grid
- 140 million tons of material to construct batteries
- 6 pounds of technical-grade Lithium Carbonate is needed per nominal kWh
- Each vehicle battery pack will need about 60 lbs. of cobalt
- Reliance on foreign sources as Lithium and cobalt are rare earth metals not mined extremely in the U.S.
- Add 300-350 lbs. of plastic for insulation and packaging per vehicle battery system
In any case, switching from fossil fuels to renewable energy reduces ecological damage but does not eliminate it. For example, even solar cells and windmills do damage the environment since solar cells require toxic substances to be manufactured and windmills can have
environmental impacts including the potential to reduce habitat for wildlife, fish and plants.
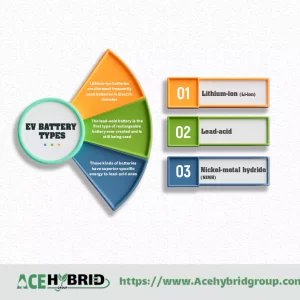
They can also harm migrating birds. Also, battery technology currently requires Lithium and other rare earth metals which must be mined.
None of these technologies are perfect.
Overall, electric cars play an important role in consumption growth and clean environment development. Promoting electric mobility and advancing sustainable EV technologies are highly anticipated, but powerful auto lobbies support policies that help automakers sell more cars, something which hampers efforts to protect the environment. However, the large-scale development of battery-electric vehicles are linked to policy measures and government incentives.
Credit: Forbes
 Ace Hybrid Tech | Hybrid battery replacement
Ace Hybrid Tech | Hybrid battery replacement